Maryland’s Oyster Restoration Sanctuaries Show Promising Signs for Shellfish Recovery
At restoration sites, oysters are establishing dense, productive reefs
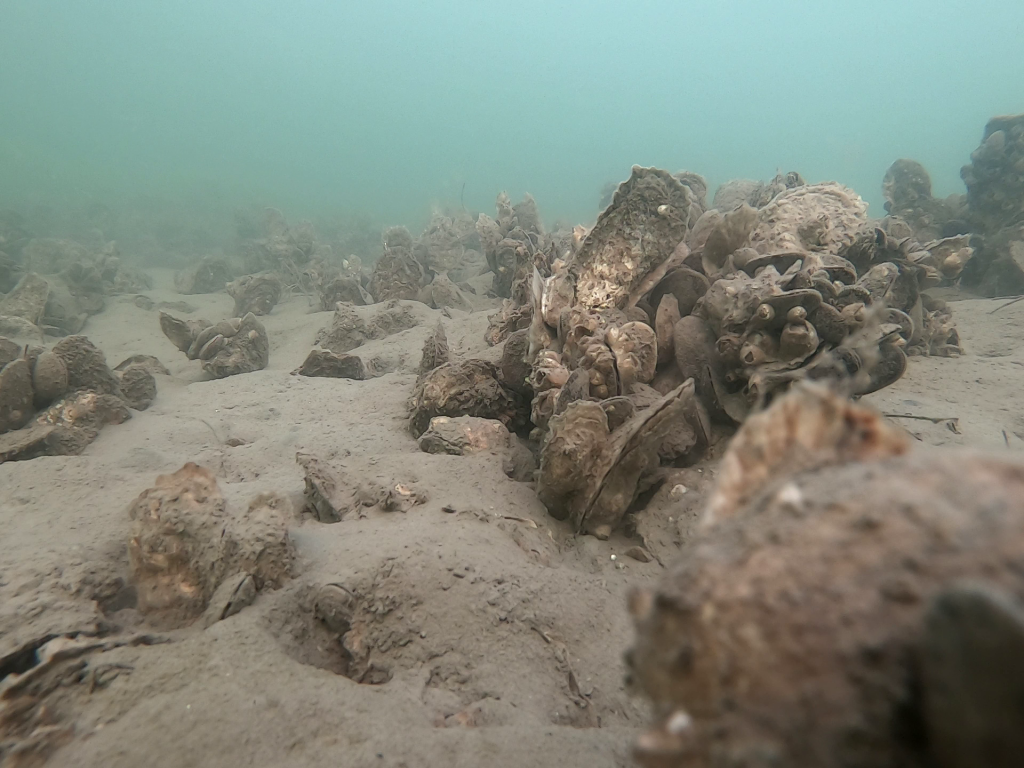

A restored oyster reef in the Harris Creek sanctuary in 2021. In a thriving oyster reef, oyster shells accumulate into three-dimensional structures where crabs scuttle, sea squirts dangle and fish dart through clearings. Like coral reefs, oyster reefs support an ecosystem that flourishes around them. Photo by the Smithsonian Environmental Research Center.
At first, oyster biologists were concerned. Monitoring efforts at some restoration sanctuary reefs in 2022 weren’t pulling up many oysters, even though the sites had previously been performing well.
So divers with the Oyster Recovery Partnership went into the water to investigate. What they found there wasn’t a shortage of oysters, but such a dense and mature population that the shellfish had cemented into three-dimensional reefs, thick enough that the team’s patent tongs sampling gear weren’t able to get them out of the water.
“We’re excited because we feel like we’re starting to reach our goal of self-sustaining reefs,” said Olivia Caretti, the partnership’s coastal restoration program manager. “In another sense, it becomes a question of how we adjust our sampling plan. It’s a good problem to have.”
These sites in the Tred Avon River are a part of an ongoing and long-term experiment in oyster recovery. In an effort to shore up declining numbers of the bivalve, Maryland dramatically expanded oyster sanctuaries in 2010 to cover 24% of historic oyster habitat in the Bay, a span of about 9,000 acres spread over a wide geographical area.
Then, in June 2014, Maryland and other regional governments signed onto the Chesapeake Bay Program’s Chesapeake Bay Watershed Agreement that outlined a goal to “restore habitat and populations in 10 tributaries by 2025 and ensure their protection.”
Maryland and Virginia split these 10 tributaries, and both states embarked on five large-scale restoration projects. In Maryland, these are known as the “Big Five” sanctuaries in Harris Creek and the Little Choptank, Tred Avon, St. Marys, and Manokin rivers.
Now, nearing 10 years after the agreement, Maryland’s restoration sanctuaries are on track to be completed in time to meet next year’s goal. Across these restoration sanctuaries, scientists are finding impressive signs of recovery, with considerable reproduction and the establishment of dense, vertical oyster reef structure.
“The success of these restoration sanctuaries is a testament to years of dedicated work,” said Maryland Department of Natural Resources Secretary Josh Kurtz. “DNR and our partners are taking oyster restoration seriously, and it’s great to see our efforts result in these productive, living reefs.”
The restoration work is carried out by the Chesapeake Bay Program’s Maryland Oyster Restoration Interagency Workgroup, a partnership between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Baltimore District, the Oyster Recovery Partnership and the Maryland DNR.
Of Maryland’s Big Five restoration sanctuaries, initial restoration is complete at four, and Harris Creek is considered fully restored. In 2022, Harris Creek had an average density of 462 oysters, including spat and small oysters, per square meter.
At the fifth large-scale restoration sanctuary, Manokin River, initial restoration work began in 2021 and DNR estimates it will continue until 2025.
Evaluating the Oyster Restoration Sanctuaries
The restoration sites are exceeding success metrics established by the Maryland Oyster Restoration Interagency Workgroup. The workgroup’s 2021 Oyster Monitoring Report on these large-scale restoration sites showed that 100% of 3-year-old and 6-year-old reefs that year met the minimum success criteria for oyster density–15 oysters per square meter over 30% of the reef area. More than 90% of the reefs had more than 50 oysters per square meter in the same area.
The 2022 and 2023 reports are scheduled to be released this spring, but DNR scientists think it’s likely that the trends already seen will continue.
“The five large scale sanctuaries have significant populations of oysters, given the massive plantings and the occurrence of natural spatset,” DNR Shellfish Division Director Christopher Judy said. “The next monitoring report will likely show a continuation of past results.”
DNR’s own oyster monitoring across the Bay has found that restored sanctuaries are high in oyster density, reproduction, and cultch (the shell or substrate necessary for juvenile oysters to grow on) as well as low in mortality.
From 2012 to 2022, DNR spent $49 million to restore oysters in the five large-scale sanctuaries. By the end of 2022, partners had planted 5.93 billion juvenile oysters and created 894 acres of oyster reefs at the Big Five sanctuaries, according to the working group’s 2022 Chesapeake Bay Oyster Restoration Update. Previously, these sites had only 42 acres of existing reefs that met the restoration metrics, which did not require initial restoration.
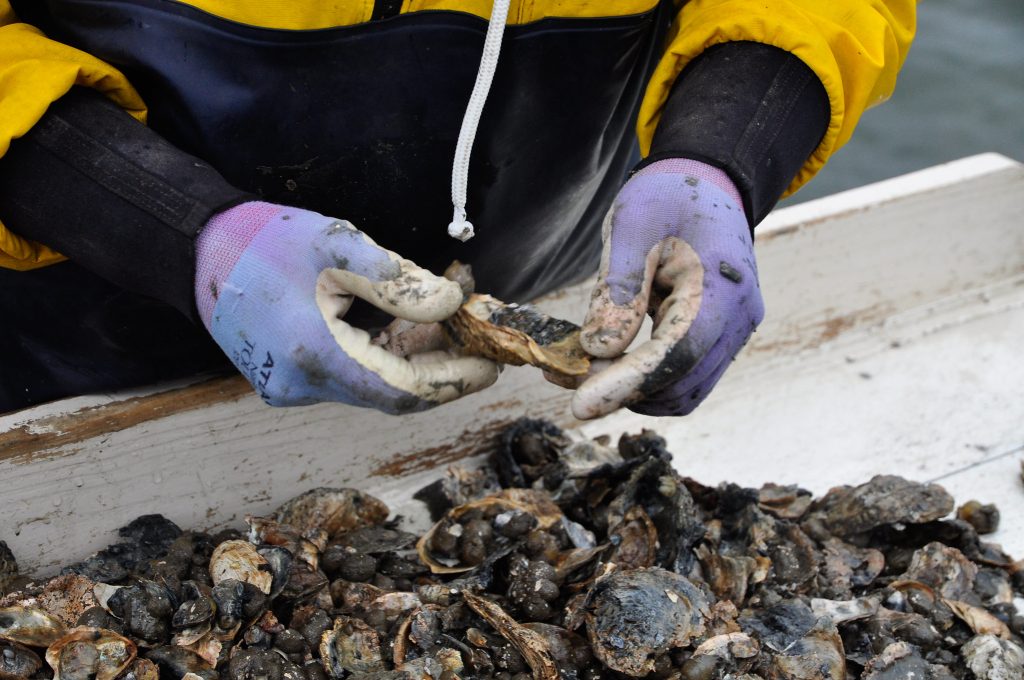

A DNR staff biologist assesses oyster shells for spat, or juvenile oysters, as part of the 2015 fall oyster survey. DNR photo by Joe Evans
The Need for Oyster Restoration
Scientists and environmental advocates say this considerable undertaking was necessary to begin to address the need for oyster recovery.
Once far more abundant in the Bay, eastern oysters plummeted to a fraction of their early-1800s population due to historic overharvesting, disease-related mortality, habitat degradation, and reduced water quality.
The bivalve is a keystone species, a critical part of the ecosystem of the Bay, as well as an economic driver for the region, making restoration a priority. Oysters also serve as natural filters in waterways. Scientists estimate that adult oysters can filter more than 10 gallons per day in the Chesapeake Bay.
Sanctuaries are permanently closed to harvest, except on aquaculture lease sites, and intended as areas where oysters can grow undisturbed. This enhances the oyster broodstock population and allows the bivalves to build reefs that offer crucial habitat to many other Bay species.
Scientists hope that sanctuaries could also help facilitate pockets of natural disease resistance. In theory, oysters that survive after an outbreak of an oyster disease could better pass on their resistance if left undisturbed in a sanctuary setting. The diseases MSX and Dermo lead to significant die-off in Chesapeake Bay oysters in previous decades.
Restoring a sanctuary involves building cultch, the hard substrate that can support reefs, and planting spat, or juvenile oysters. The University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science’s Horn Point Laboratory in Cambridge grows most of the oysters that supply these restoration efforts.
This fall, DNR’s annual dredge survey on juvenile oysters found prolific spatfall across a wide distribution of the Bay, both in numerous harvest areas and sanctuary areas. (Spatset or spatfall refers to oyster reproduction in an area.) It was the fourth consecutive year of above-median results for juvenile oysters. Data from the survey also indicates that sanctuaries are performing about on par with previous levels and expectations.
Environmental conditions in the Bay, such as higher salinity, have been more favorable to oysters in recent years, likely playing a major part in the increased spatfall. But research suggests that restored sanctuaries provide areas where oysters can thrive in the long term, especially when these environmental conditions are right.
Visualizing Oyster Restoration
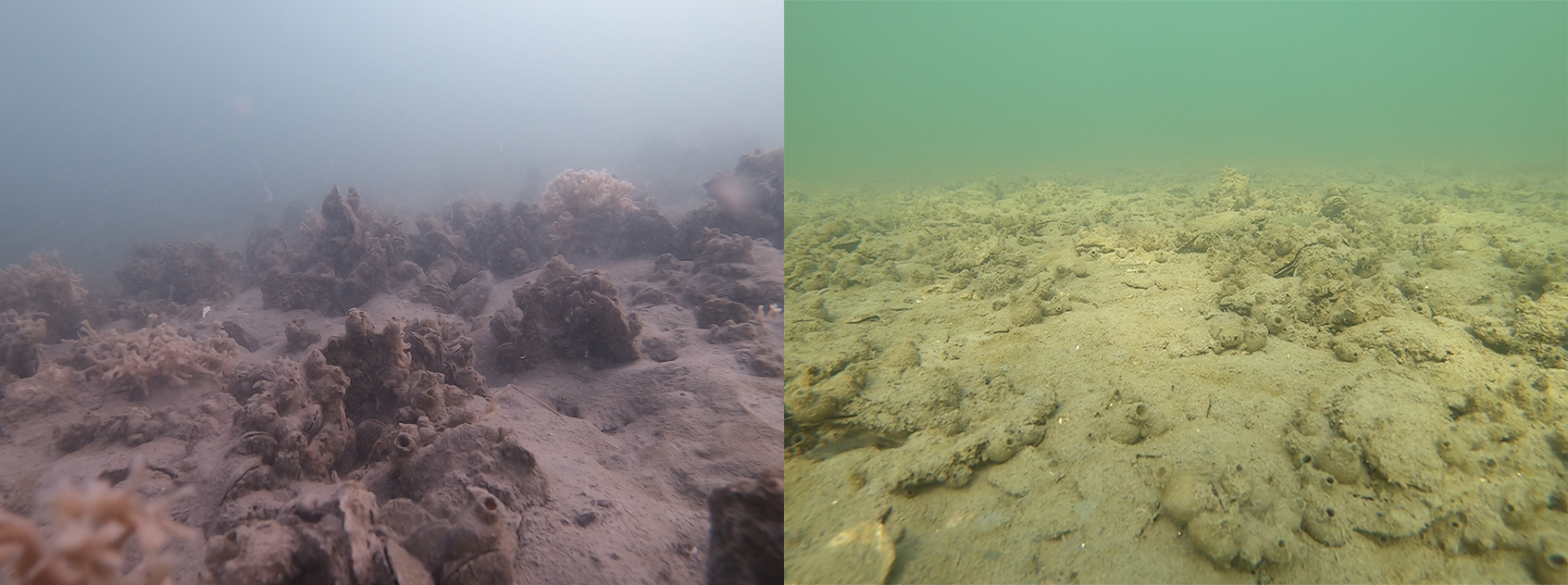
Using underwater photographs from tributaries of the Chesapeake in Maryland and Virginia, scientists at the Smithsonian Environmental Research Center analyzed oyster habitats at 600 sites, including areas that were restored and unrestored, as well as sanctuaries and harvest locations.
Comparing the percent of the bottom covered by oysters and the amount of verticality—which indicates the buildup of reef structure—at these sites, restored sanctuaries performed notably well.
“Generally the reefs that are in the best condition at a Chesapeake-wide scale are the ones that are both protected from harvest and have seen restoration,” said Matt Ogburn, a senior scientist at the Smithsonian Environmental Research Center and an author of the study, which was published in October in Marine Ecology Progress Series.
Oysters form reefs on older shells or other hard surfaces, and these structures grow vertically over time. These oyster reefs form the foundation of an underwater ecosystem, providing habitat for fish, crabs, shellfish, and other marine life. The reefs act as nurseries for small fish and hunting grounds for larger fish, which makes for prime angling for sport fish like striped bass and black drum.
Vertical reefs also provide more space for oyster spat to grow, which in turn leads to increased density. Vertical reefs allow the mollusks to stick up higher in the water and have greater access to algae, increasing water filtration, Ogburn said.
Sites that are harvested rarely have this vertical structure, Ogburn said. Harvest sites might be covered in oysters, but they’re all laying down flat at the bottom.
“A core finding of our study was that when oysters are protected from harvest like in the sanctuaries, those oyster reefs all look really good,” Ogburn said. “They often meet the restoration metrics or exceed them, and they also support other species.”
Can Restoration Sanctuaries Reseed Oyster Harvest Areas?
While sanctuaries have seen positive growth, it’s not yet clear how sanctuaries are affecting the overall oyster population in the Bay. Most sanctuaries are relatively new, and DNR scientists suggest that it will take time to gather all the data and have a better understanding of the Bay-wide benefits of sanctuaries.
The next five-year report will come out in 2026, and DNR scientists will analyze that data to determine if there are any indications that restored sanctuaries are contributing to spatset outside sanctuary boundaries. The DNR Shellfish Division has also been planting half-acre shell sites outside the Big Five sanctuaries since 2018, which could help demonstrate whether spat is spreading, either from sanctuaries or harvest areas.
When oysters reproduce, they release eggs and sperm into the water column. Fertilized eggs then develop into free-swimming larvae that drift in the water for two to three weeks before latching onto a hard surface—often other oyster shells. There, the larvae develop into mature oysters and remain sessile, locked in the same spot, for the rest of their lives.
A model developed by researchers at the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science suggests that larval oysters are able to spread widely before settling down.
Oyster larvae are extremely small—tinier than a grain of sand—and scientists can’t follow them in the water, said Elizabeth North, a professor at the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science who studies the influence of water flow on oyster larvae in the Chesapeake Bay. But the movement of the larvae can be estimated.
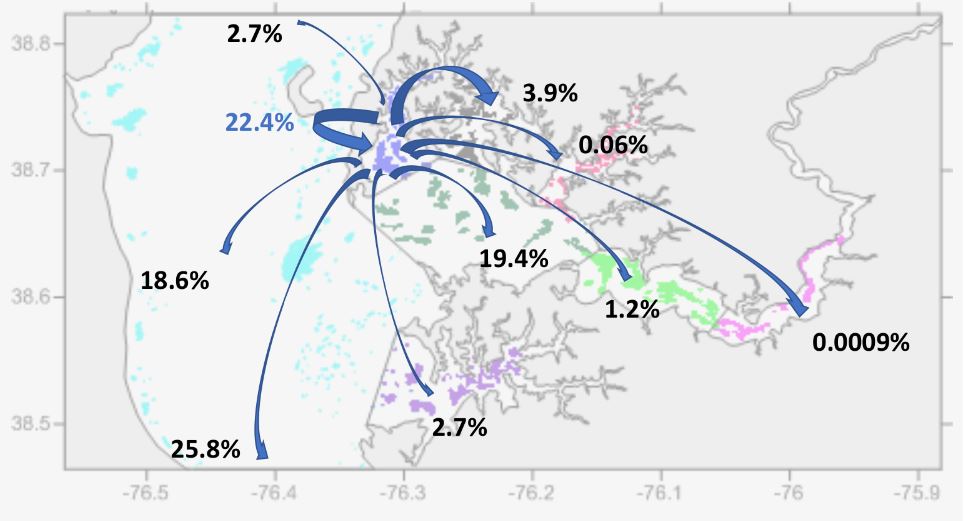
The percent of simulated larvae released from Harris Creek estimated to settle into other regions or back to the sanctuary (blue percentage). Via Elizabeth North, University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science
With a simulation that took into account tides, river flow, salinity, temperature and a number of other factors, North’s team predicted that greater than 95% of larvae end up leaving their reef of origin and settle somewhere else.
Oysters benefit from having a network of reefs that act as “landing strips” to catch larvae as they drift, North said. Some reefs are naturally suited, because of their size or position in the water, to be the “population hubs” that send larvae to other reefs, while others collect larvae but don’t contribute as many to other reefs. Restoration efforts have created new “landing strips” for oyster larvae.
North said oyster larvae are certainly leaving from restoration sanctuaries, though it’s not yet clear how much the larvae then populate the oyster bars of the commercial fishery, or how many of the larvae from commercial areas populate the sanctuaries that have “landing strips” in them.
“There’s no doubt in my mind that any reefs that have oysters on them, especially high density, 50 per square meter and higher, are broadcasting larvae to other areas,” she said.
Restoration and the Long-Term Outlook for Oysters
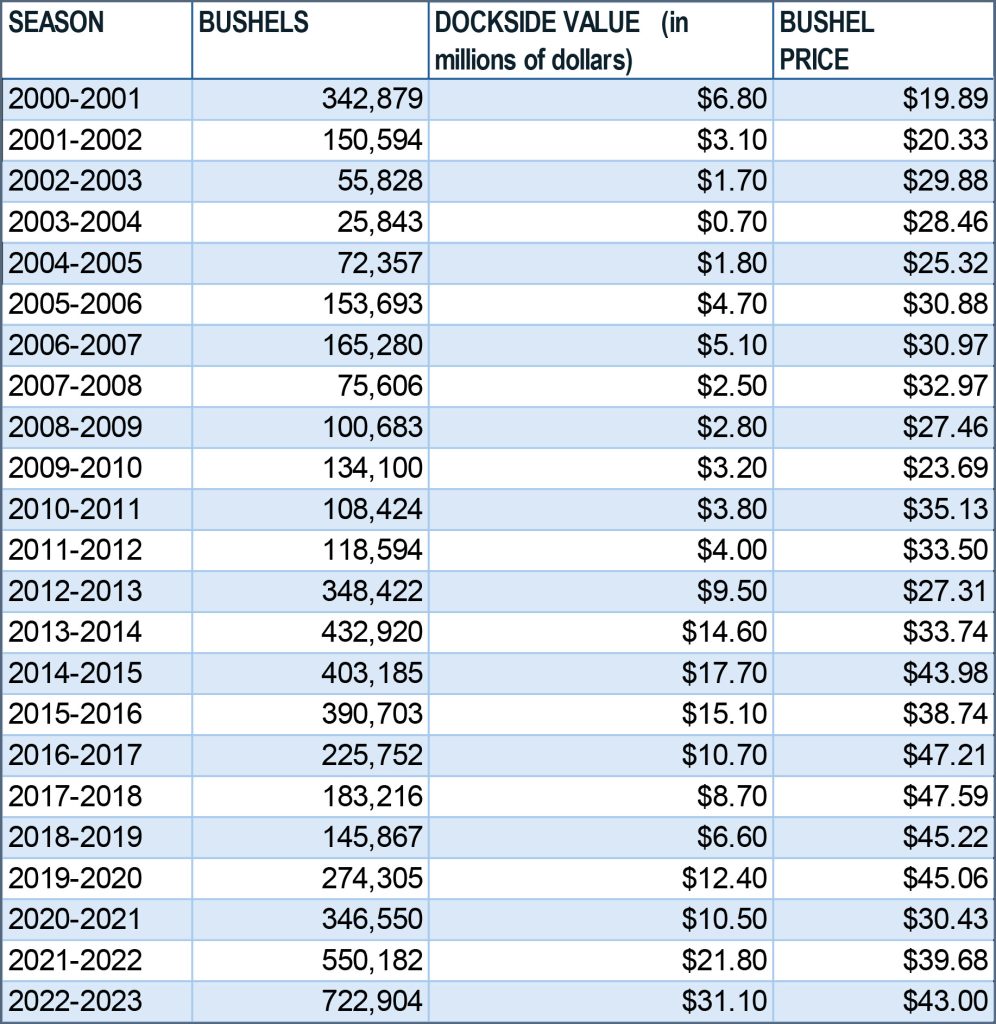
Though the Chesapeake Bay oyster population continues to face challenges, there have been other promising signs for oysters, aside from spatset numbers and reef growth. In the past two seasons, Maryland oystermen have brought in the highest number of oysters since 1987, at least in part due to successive years of good spatsets that generated increased numbers of oysters.
The 543,000 bushels in 2021-2022 and 722,000 bushels last winter resulted in a dockside value of $21.5 million and $31 million, according to the DNR Shellfish Division.
The spatset in 2023 marked the fifth highest in 39 years, with a historic geographic distribution that far exceeded prior spatsets, a recent milestone in natural oyster reproduction in the Bay. Shellfish biologists were finding spat in areas where they were rarely observed, including in the upper reaches of some Bay tributaries that are typically too brackish for strong oyster reproduction.
And restoration efforts continue apace. Last year, a record 1.7 billion new juvenile oysters produced at state hatcheries were planted on sanctuary and public oyster fishery sites in Maryland’s Chesapeake Bay.
Aside from restoration sanctuaries, there are some unrestored sanctuaries that are doing well. The Nanticoke River sanctuary, which received some limited small-scale restoration since 2020, had an average density of 417 oysters per square meter in 2022. Hooper Straits sanctuary, which received no restoration, had an average density of 294 oysters per square meter in 2022.
But some other sanctuaries that have not received restoration are performing less well. These sites tend to be in lower salinity areas, which are less favorable to oyster reproduction, or in places that didn’t have a lot of good oyster habitat prior to 2010.
But DNR scientists say these sites also present opportunities to get more oysters in the water and further restoration efforts.
“Right now, we have considerable unrestored sanctuary areas that are unproductive because they lack suitable substrate,” said DNR Fishing and Boating Services Director Lynn Fegley. “These areas will need investment to begin producing oysters, and this could come in the form of restoration sanctuaries or in the form of multi-use areas that include aquaculture and some wild harvest. The overarching goal is more oysters in the water and improved ecological function.”
In February, the Chesapeake Bay Foundation released a report calling for additional oyster restoration in Maryland and Virginia, highlighting the benefits oysters provide economically and environmentally, including their ability to protect shoreline habitats from erosion. The Chesapeake Bay Program will determine and approve any new goals for the Bay.
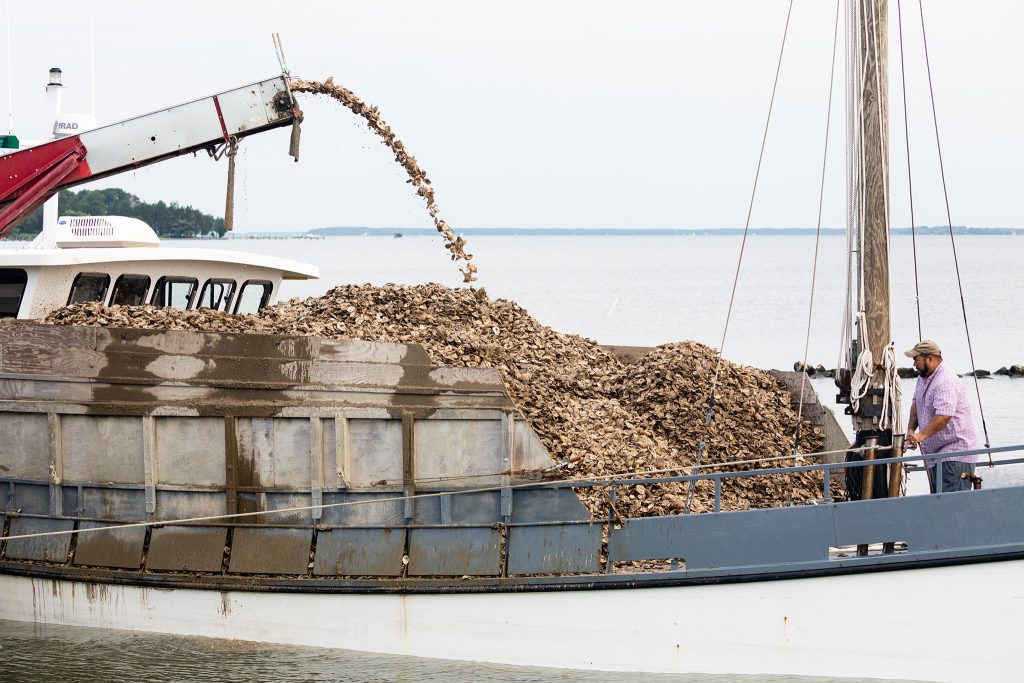

Crewmembers load recycled oysters onto the deck of the Poppa Francis at the Horn Point Oyster Hatchery in Cambridge in 2022. The oyster shells were laden with 20 million spat for seeding a reef in the Tred Avon River sanctuary. Photo by Will Parson/Chesapeake Bay Program
Smaller-scale restoration projects are in the works. In January, DNR committed to planting 147 million oyster spat in Herring Bay Sanctuary with mitigation funds from the Ever Forward running aground on an oyster bar in March 2022.
Cody Paul, a Dorchester County waterman who’s harvested oysters for 13 years, has worked with the Oyster Recovery Partnership on monitoring in the Choptank and Tred Avon rivers and Harris Creek. He said that, although sanctuaries remove bottom areas from harvest, he sees the benefit of them too, from helping build the overall broodstock of oysters to contributing to water filtration.
“The first time I ever went, it was jaw-dropping what you would see there,” he said of the sanctuaries.
Ben Ford, the Miles-Wye Riverkeeper with the environmental nonprofit ShoreRivers, has monitored and captured footage at oyster sanctuaries on the Eastern Shore and said he’s impressed by the recovery he’s seen.
“Oysters loom so large in our culture and our history and our environment,” he said. “So it’s great to give back and have that persist. I know it sounds trite, but for our kids and their kids—I have an almost 2-year-old and I want him to see what I’m seeing, and maybe something even better.”
By Joe Zimmermann, science writer with the Maryland Department of Natural Resources.




 1-888-373-7888
1-888-373-7888 233733
233733