July 2019 Hypoxia Report
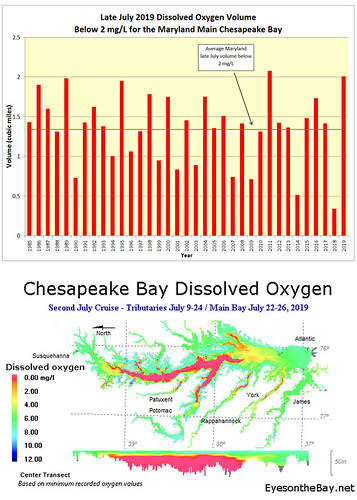
 Maryland Department of Natural Resources monitoring data show that dissolved oxygen conditions in the Maryland portion of the Chesapeake Bay mainstem were larger than average in July, as the result of many factors. The hypoxic water volume (areas with less than 2 mg/l oxygen) was 1.92 cubic miles in early July and 2.01 cubic miles in late July. The early July 1985-2018 average hypoxic volume is 1.36 cubic miles, and late July is 1.34 cubic miles. The most recent hypoxic volumes were respectively the fourth-largest for early July and second-largest for late July since 1985.
Maryland Department of Natural Resources monitoring data show that dissolved oxygen conditions in the Maryland portion of the Chesapeake Bay mainstem were larger than average in July, as the result of many factors. The hypoxic water volume (areas with less than 2 mg/l oxygen) was 1.92 cubic miles in early July and 2.01 cubic miles in late July. The early July 1985-2018 average hypoxic volume is 1.36 cubic miles, and late July is 1.34 cubic miles. The most recent hypoxic volumes were respectively the fourth-largest for early July and second-largest for late July since 1985.
Larger than average hypoxia was predicted for this summer in part due to massive rainfall causing high flows into the Chesapeake Bay the past year, which delivered higher nutrient loads. Those nutrients fuel algal blooms, which die and are consumed by bacteria, which then deplete oxygen in bottom waters. Also, average winds were generally low in July, which prevented oxygen from mixing into deeper waters.
In late July, just prior to sampling, air temperatures reached 100 degrees for several consecutive days, heating main bay waters to near 90 degrees. Warmer water holds less oxygen. Finally, surface salinities have been below average for Maryland’s main bay, which creates a more stratified water column, essentially acting as a cap to prevent higher oxygen surface waters from mixing with deeper, oxygen-depleted waters.
In the beginning of June, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, United States Geological Survey, University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science and University of Michigan scientists predicted a large hypoxic volume for the bay in 2019 due to higher flows last fall and this spring, and higher nitrogen loading from the Susquehanna and Potomac rivers.
Crabs, fish, oysters and other creatures in the Chesapeake Bay require oxygen to survive. Scientists and natural resource managers study the volume and duration of bay hypoxia to determine possible impacts to bay life. Each year (June-September), the Maryland Department of Natural Resources computes these volumes from data collected by Maryland and Virginia monitoring teams during twice-monthly monitoring cruises. Data collection is funded by these states and the Environmental Protection Agency’s Chesapeake Bay Program. Bay hypoxia monitoring and reporting will continue through the summer.

 The Maryland Department of Natural Resources also provided regular updates on Chesapeake Bay monitoring through its new Eyes on the Bay subscription newsletter.
The Maryland Department of Natural Resources also provided regular updates on Chesapeake Bay monitoring through its new Eyes on the Bay subscription newsletter.
